Heap
The Java virtual machine heap is the area of memory used by the JVM (and specifically HotSpot) for dynamic memory allocation.[10] The heap is split up into "generations":
- The young generation stores short-lived objects that are created and immediately garbage collected.
- Objects that persist longer are moved to the old generation (also called the tenured generation).
- The permanent generation (or permgen) is used for class definitions and associated metadata.[11][12]
Originally there was no permanent generation, and objects and classes were stored together in the same area. But as class unloading occurs much more rarely than objects are collected, moving class structures to a specific area allows significant performance improvements.[11]
source -
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_virtual_machine
How do you determine a good MaxPermSize?에서 Matt 가 OOM(OutOfMemory) 에러에 시달리는데, -Xmx 사이즈를 아무리 늘려도 해결이 안됐었나 보다.
설명에 의하면 클래스의 메타 정보는 -Xmx 로 지정되는 메모리 영역이 아닌 MaxPermSize로 지정되는 메모리 영역에 들어간다고 한다.
헌데, 요즘, Spring, iBatis, Hibernate 같은 리플렉션을 이용해서 클래스 메타 정보를 가져다 쓰는 프레임워크들이 많아지면서, MaxPermSize 를 기본값으로 놓고 사용하면 메모리가 부족해지는 현상이 일어나나 보다(나는 아직 겪어보지 못했다).
-XX:PermSize=64m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m
위와 같이 MaxPermSize를 지정하면 된다.
근데, 댓글들을 읽어보면 256m 은 좀 오바인것 같고, OOM 오류가 발생하면 테스트를 해가면서 세팅해야 할 것 같다.
기본 값은 JVM이 -client 옵션의 경우에는 32m -server 옵션일 경우에는 64m 이라고 한다.
또한, MaxPermSize는 -Xmx 로 지정한 메모리 용량과 별도로 할당된다. 즉, -Xmx가 256m 이고, -XX:MaxPermSize가 256m 이라면, 최대 512m이 할당될 수 있다는 것이다.
MaxPermSize and how it relates to the overall heap에 MaxPermSize에 대한 더 자세한 내용이 있다.
JAVA(J2SE 1.4.1) 메모리 영역 구조도 함 읽어보자.
출처 -
http://kwon37xi.egloos.com/2368729
이번에는 Heap dump를 통해 분석할 수 있는 경우로 Permanent 영역 Full 문제를 분석하는 방법에 대해 사례를 통해 알아 보도록 하겠습니다.
이전 포스트에서 설명드렸듯이 Permanent 영역은 Class의 메타정보들이 저장되는 영역이며, 이는 JVM에서 class 정보를 토대로 메모리 상에 object로 생성할 때 효과적으로 빠르게 생성하기 위해 저장하는 것입니다.
Permanent 영역 Full도 일종의 OutOfMemoryError의 한 종류이며, 설정한 Permanent 영역의 크기보다 더 많은 class들을 사용하고 있을 경우 발생할 수 있읍니다. 또한 잘못된 Custom ClassLoader 구현으로 인해 중복된 class 정보들이 해제되지 못하고 지속적으로 메모리를 잠식하는 경우가 있습니다.
Permanent 영역의 크기보다 더 많은 class들을 사용하고 있을 경우는 Permanent 영역의 크기를 늘려주기만 하면 됩니다. 그러나 그렇지 않은 경우는 문제를 분석하여 어느 부분에서 해제를 못하고 있는지를 확인해야 합니다.
바로 이부분이 이번 포스트에서 다룰 내용입니다.
사실 이러한 문제는 해결하는 것이 그렇게 쉽지는 않습니다. 제가 이번 포스트에서 설명드릴 사례도 정확하게 어느 부분에서 문제가 발생하였는지 확인하지 못한 경우입니다. 저의 능력이 거기까지 였던거 같습니다. ㅠ.ㅠ!
Permanent 영역 Full 오류가 발생하면 다음과 같은 오류가 로그파일에 출력됩니다.
그럼 지금부터 Permanent Generation Full 오류 문제를 Heap dump를 통해 분석하는 방법에 대해 사례를 통해 알아 보도록하겠습니다.
분석 방법에 대한 이해를 높이기 위해 분석 사례의 오류 발생 상황에 대해 먼저 설명드리도록 하겠습니다.
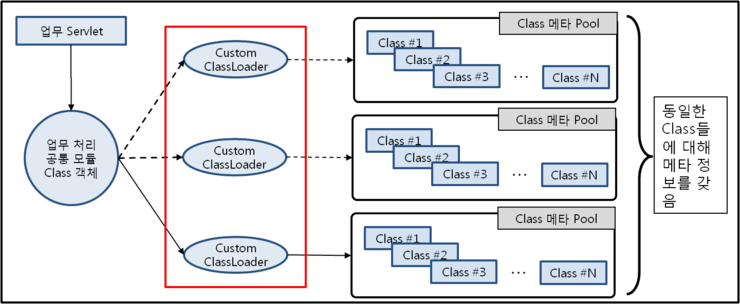
정상적이라면 Custom ClassLoader가 하나만 생성되어 있어야 하지만 동일한 Custom ClassLoader가 여러개 생성되어 동일한 class의 메타 정보가 여러 Custom ClassLoader에 중복 생성됨으로써 Permanent 영역의 공간을 차지하고 있는 경우입니다.
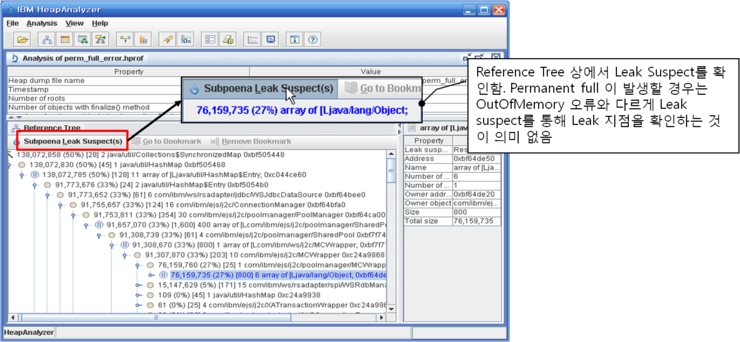
그럼 해당 Heap dump를 HeapAnalyzer 툴을 통해 분석해 보도록 하겠습니다.
위와 같이 Heap dump 파일을 HeapAnalyzer에서 열게 되면 reference tree와 함께 leak suspect 부분이 나타납니다.
그러나 Permanent 영역 Full 인 경우는 이 leak suspect가 OutOfMemoryError에서와 다르게 확인하는 것이 의미가 없습니다.
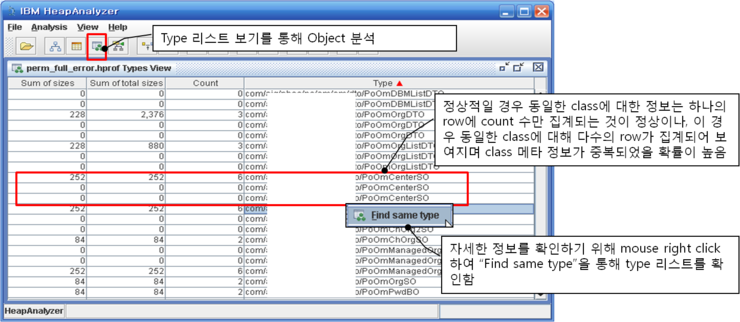
위의 그림과 같이 Permanent 영역 Full이 발생할 경우는 class 정보의 중복 여부를 확인하기 위해 Type 리스트 보기를 선택합니다.
그리고 Type 리스트에서 "Type" 즉 class 명을 클릭하여 정렬하고 class 들의 중복 여부를 확인합니다.
정상적인 경우는 동일한 class에 대한 정보는 하나의 row에 count 수(class 한개와 object 여러개)만 집계되지만 위의 경우는 동일한 class에 대해 다수의 row가 집계되어 보여지는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 이는 Type 리스트의 개별 row는 하나의 class에 대한 메모리 address로 생성됩니다. 따라서 동일한 class에 여러개의 row가 있다는 것은 하나의 class가 다른 메모리 address를 가지고 존재하고 있다는 것입니다.
즉, class가 변경되었거나 하였을때 제대로 해제되지 않았다고 볼 수 있는데요. 이렇게 동일한 class가 각각 다른 메모리 address에 존재한다는 것은 해당 class를 로드한 ClassLoader가 class의 메모리 address 수만큼 여러개일 확률이 높습니다.
그럼 동일한 class중 하나를 오른쪽 마우스 click하여 "Find same type"을 통해 확인해 보도록 하겠습니다.
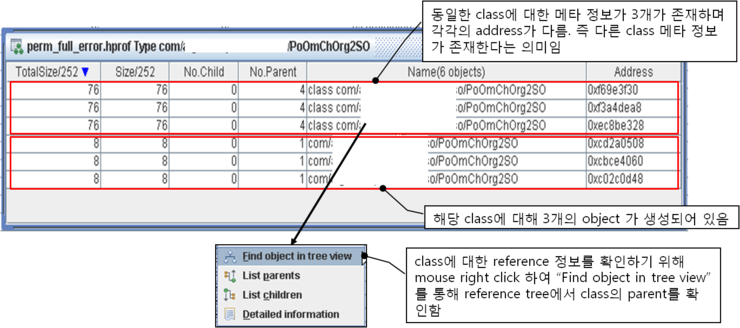
위와 같이 해당 class에 대한 동일 type의 리스트를 확인해 보면 동일한 class가 3개 존재하고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
그 아래로는 class를 토대로 생성된 object들이 3개가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 object 들이 하나의 class를 토대로 만들어 졌는지 아니면 각각의 class에 대해 하나씩 object가 생성된 것인지는 알 수는 없지만, 동일한 class가 3개가 있다는 것으로도 ClassLoader상에 문제가 있어 Permanent 영역이 언제 Full 날지 모르는 상황인것 만은 분명한 것으로 보여집니다.
그럼 각 class들에 대해 오른쪽 마우스 click하여 "Find object in tree view" 선택하여 reference tree상에서 해당 class의 위치와 계층을 확인해 보도록 하겠습니다.
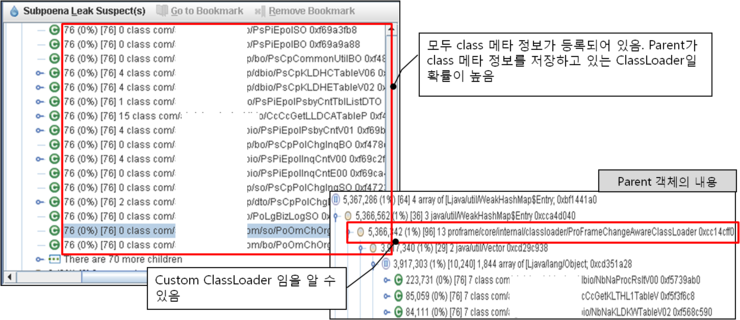
해당 class를 reference tree에서 확인해 보면 다른 업무 class들의 리스트가 존재하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
그럼 이러한 class들이 속해있는 parent object를 확인해 보면 위의 그림과 같이 Custom ClassLoader내에 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 이번 사례의 Custom ClassLoader는 개발 프레임웍인 Proframe의 ProframeChangeAwareClassLoader 입니다.
각 class들이 모두 동일한 ClassLoader에 포함되어 있는지 아니면 각각 별개의 ClassLoader에 포함되어 있는지를 확인하기 위해 각 class들을 위와 동일하게 확인하면 각각 다른 Custom ClassLoader 객체에 포함되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
그럼 각 Custom ClassLoader들이 어느 위치에 존재하는지 parent 객체를 확인하고 계층을 확인해 보도록 하겠습니다.
위의 그림과 같이 3개의 Custom ClassLoader 중 2개는 동일한 object 계층구조를 가지고 있으나, 나머지 하나는 다른 계층 구조를 가지고 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
그럼 무엇이 다른지 확인해 보도록 하겠습니다.
세개 중 다른 계층 구조를 갖는 Custom ClassLoader는 정상적인 것을 보여집니다. ClassLoader가 가져야할 계층 구조(Thread --> AppClassLoader --> ContextFactory --> Custom ClassLoader ...)이나 나머지 두개는 AS400과 관련된 객체(IBM Toolbox for java)를 parent로 가지고 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
AS400 관련 객체는 AS400 장비의 DB2 데이타베이스와 연동하기 위한 JDBC Driver라고 할 수 있습니다.
AS400 관련 객체가 Custom ClassLoader(ProframeChangeAwareClassLoader)를 생성하거나 참조할 경우는 없을 것 같으니 이러한 계층구조를 갖게된 것은 역참조에 의한 부분으로 보여집니다.
이러한 현상은 Hot-deploy 수행 시 Custom ClassLoader가 해제되지 않고 계속 존재하여 동일한 class들이 ClassLoader로 로드되어 Permanent 영역 Full이 나는 것입니다.
Custom ClassLoader가 해제되지 않고 존재하는 원인을 밝히기 위해서는 Custom ClassLoader와 AS400 관련 class 간의 관계를 파악할 필요가 있습니다. 그뿐 아니라 AP들과의 관계(AP 처리 flow등)도 같이 분석해야 하는 굉장히 어려운 분석 작업을 수행해야 합니다.
이번 사례는 소프트웨어 제품에 대한 분석인 관계로 접근도 용이하지 않고 분석할 수 있는 데이터도 제한이 있어 끝내 밝히지 못했던 사례입니다. 물론 벤더의 개발자가 직접 확인을 했으나 뚜렸한 원인을 파악히지 못한 경우 였습니다.
그러나 유력한 원인으로 유추해 볼 수 있는 부분은 AS400(IBM Toolbox for java) 연계 방식이 일반 JDBC와 다르게 처리 결과 응답을 별도의 응답 Thread가 기동하여 수신 처리한다는 것이며 이러한 Thread가 AS400과의 Connection 이 끊어지기 전까지는 종료되지 않으므로 이 Thread 에서 Custom ClassLoader과 관리하는 Data 관련 객체들을 사용하게 되면 Custom ClassLoader의 역참조가 발생하는 것이 아닌가 하는 것입니다. 물론 아닐 수도 있겠지만 ㅠ.ㅠ!
사례에 대해 깔끔한 원인 분석은 이루어지지 않았지만 여기까지가 저의 한계라고 생각하며 사례에 대한 부분은 마치도록 하겠습니다.
그리고 지금 부터는 번외로 ClassLoader에 대해 간단히 설명을 드리도록 하겠습니다.(이후 포스트에서 자세히 다룰 예정입니다.)
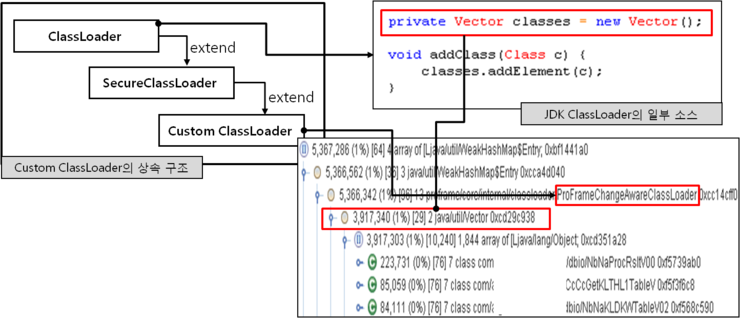
다음은 ClassLoader와 Permanent 영역간의 관계에 대한 이해를 위해 Custom ClassLoader와 class 메타 정보가 저장되는 Vector 객체에 대한 그림입니다.
앞의 사례에서 Custom ClassLoader는 실제로 class 메타 정보를 저장하기 위해 JDK의 ClassLoader를 상속받아 구현하게 됩니다. ClassLoader 객체내에 Vector가 있으며 이 Vector가 class들의 저장소 역할을 하며 이 Vector의 내용을 확인하여 class가 이미 로드되었는지 아닌지를 확인하게 됩니다.
그럼 Custom ClassLoader는 무슨 기능을 할까요? 말 그대로 각종 ClassLoader의 기능을 구현하는 것입니다. 예를 들어 class cache 기능 또는 class 변환 기능 등 다양한 기능을 class를 로드하기 전이나 후에 수행할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 Custom ClassLoader는 ClassLoader를 상속받아 구현되며, Permanent 영역 Full이 발생할 경우 Custom ClassLoader내에는 아래와 그림과 같이 Vector 객체에 class들이 위치하는 것은 일반적인 현상입니다.
이상으로 Permanent 영역 Full 문제를 Heap dump를 통해 분석해 보았습니다.
다음에는 Heap 메모리 Leak에 대해 알아볼까 생각중입니다.
그럼 모두들 즐거운 일상되시기 바랍니다.
출처 -
http://blog.naver.com/bumsukoh?Redirect=Log&logNo=110125469644
메모리 누수 leak 를 알게 되는 일반적인 방법 중 하나가 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError 에러 입니다. 이
에러는 Java 힙 heap 이나 힙의 특정 영역에 객체를 할당 할 수 있는 공간이 충분하지 않을 때 발생합니다.
PermGen space 라는 메시지는 permanent generation 이 가득 찬 상태라는 것을 알려줍니다. permanent generation 은 클래스와 메쏘드 객체가 저장되는 힙의 영역입니다. 어플리케이션이 많은 수의 클래스를 로드하면, -XX:MaxPermSize 옵션을 사용하여 permanent generation 의 크기를 증가시킬 필요가 있습니다.
톰캣 Tomcat 을 사용하다 이 에러를 보았다면 대체로 웹 어플리케이션을 너무 많이 Update 하거나 Reload 한 것이
원인입니다. 톰캣 과 JVM 은 웹 어플리케이션을 삭제하고 다시 생성할 때 할당한 모든 메모리를 해제하지는 않습니다. 톰캣을 여러
번 리로드하면 할당된 메모리가 바닥나서 동작하지 않게 됩니다.
톰캣에서 이 에러가 발생했을 때 해결 방법은
1. 톰캣을 재시작하는 것입니다.
2. 톰캣이 할당할 수 있는 메모리를 늘려줄 수도
있습니다. 이 방법은 에러 발생을 중지시키는 것이 아니라 톰캣을 재시작하기까지의 시간을 연장시킬 뿐입니다.
3. 메모리 누수가
발생하지 않도록 톰캣을 설정합니다.
Java Heap 크기 증가
커맨드라인으로 톰캣을 실행시킨다면 아래의 파라미터를 추가합니다.
-Xmx512m -Xms512m -XX:PermSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m -XX:NewSize=128m
윈도우 서비스로 톰캣을 실행시킨다면 톰캣 모니터를 실행시키고, Tomcat -> Java -> Java Options 에 아래의 내용을 추가합니다.
-Xmx512m -Xms512m -XX:PermSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m -XX:NewSize=128m
참고1: 복사해서 붙여넣기를 할 때 빈 공간이 추가되지 않도록 주의하십시오. 톰캣을 시작하지 못할 수 있습니다.
참고2: 64비트 버전의 톰캣을 사용한다면 레지스트리 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Apache Software Foundation\Procrun 2.0\Tomcat5\Parameters\JavaJVM 을 변경해야 합니다.
리눅스 linux 나 유닉스 unix 환경에서 톰캣 tomcat 을 사용하시면 catalina.sh 파일의 상단에 아래의 문장을 추가해 주면 됩니다. 필요에 따라 서버의 swap 영역을 넓혀줍시다.
JAVA_OPTS="-Djava.awt.headless=true -server -Xms512m -Xmx1024m
-XX:NewSize=256m -XX:MaxNewSize=256m -XX:PermSize=256m
-XX:MaxPermSize=256m -XX:+DisableExplicitGC"
메모리 누수 방지 설정
conf/web.xml file 파일에서 jsp 서블릿 부분에 아래의 내용을 추가합니다.
<init-param>
<param-name>enablePooling</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
다른 옵션에 대해서는 천천히 설명하도록 하겠습니다.
출처 - http://mindasom.tistory.com/96
출처 : http://www.javaservice.net/~java/bbs/read.cgi?b=was&c=r_p&m=appserver&n=1076057072
제목 : MaxPermSize 관련 문제
글쓴이: 최우석(guest) 2004/02/06 17:44:32 조회수:1572 줄수:26 |
|
안녕하세요.
현재 HP-UX 11.0에서 운영하고 있는 WAS 3.5에서
Permanent generation is full...
Increase MaxPermSize (current capacity is set to: 32768K )
위와 같은 에러가 나고 있습니다.
이런 에러가 나면 서버가 Hang 걸리면서 응답이 없어져서 리스타트를 해야만 합니다.
관련 문서를 찾아보니,
jvm parameter를 추가적으로 설정해 줘야한다고 하는군요.
(보시다시피 default가 32메가인 것 같습니다.)
그래서 -XX:MaxPermSize=<size>를 추가해주려고 하는데,
얼마나 설정해 줘야할 지 모르겠습니다.
ibm 문서를 검색해 봐도 HP 에서 얼마를 설정해줘라하는 문서는 못 찾겠습니다.
도움이 될만한 문서로는,
solaris에 WAS 4.0 깔 때 64m로 설정하라는 게 있었고,
WPS에서는 128m로 하라는 게 있었구요,
Xmx(현재 512m)보다 작아야한다는 것도 있었습니다만,
정확한 guideline은 없더군요.
이럴 때 어떻게 하면 좋을까요? |
제목 : Re: 운영중에 발생한 문제라면..
글쓴이: 손님(guest) 2004/02/09 11:33:26 조회수:841 줄수:28 |
|
Perm Size(Permanant Area라고 하던가요?)는 보통 WAS나 JVM이 사용하는
Class들이 사용하는 공간입니다.
보통 WAS를 처음 구동시킬때 위와 같은 에러가 발생하면, Class를 로딩시킬
메모리 공간이 부족하는 의미이며, 이때는 MaxPermSize를 어느정도 크게 잡아서
재 구동시키면 됩니다.
근데, 문제는 위와 같이 운영중인 서버에서 해당 에러를 발생시키고 죽는 경우입니다.
사실 이론적으로는 운영중일때는 위와 같은 에러메시지를 내지 말아야 하지만,
제가 추측하건데.. 다음의 경우에 발생할 수 있는듯 합니다.
첫번째는 해당 WAS의 버그때문에 운영중에 Class를 로딩을 계속 시키는 경우입니다.
모 사이트에서 모 WAS의 버그를 확인한 적이 있습니다.
그때, JSP를 .java 파일로 바꾸고 다시 컴파일하고 Class 로딩하는 WAS의 작업에
버그가 있어서, 특정 JSP에서 변환된 .class 파일이 계속 클래스로딩되었던 적이
있습니다. 이때 개발쪽하고 WAS 업체하고 말이 많았는데, 결국 WAS쪽 버그로 판명
되었습니다.
그리고, 위의 경우가 아니라면, 혹시 서비스 하는 모듈 중에 Class 로딩을 계속
수행하고 있는 것이 있는지 확인해 보십시오.
JSP 파일 자체가 계속 수정된다거나.. 인위적으로 특정 Class를 로딩시킨다던가..
아무튼, 제가 아는 바로는 운영중에 위와같은 에러가 발생한다는것은
MaxPermSize를 아무리 크게 잡아줘도 언젠가는 다시 발생할 수 있다는 것을 말합니다.
저도 이 부분에 대해 확실히 알고 싶은데, 정보가 잘 없더군요.
더 잘 아시는분이 있으시면 좋겠네요. |
출처 - http://bambabo.blog.me/120137349324
이클립스 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space 에러시
|
|
JVM메모리는 Java Heap space, Permanent Generation 이 존재합니다.
PermGen space는 JVM에서 관리하는 메모리 영역중 하나입니다.
Heap space는 프로그램 실행 도중 생성삭제 되는 Garbage-collected(필요없는경우 제거)입니다.
Permanent는 프로그램이 종료될때 까지 메모리를 차지하는 공간입니다.
Heap은 동적으로 메모리를 사용하게 되며 Permanent는 Class Names, internalized strings, Object등이 들어가며
PermGen도 이곳에 해당합니다.
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space의 해결책은 이클립스 실행시 메모리를 늘려주면 됩니다.
기본은 20M로 설정이 됩니다.
1. eclipse.ini 파일 설정.
javaw -vmargs -Xverify:none -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:PermSize=64M -XX:MaxPermSize=128M -XX:MaxNewSize=32M -XX:NewSize=32M -Xmx512M
2. eclipse실행 파일.
C:\eclipse\eclipse-jee-ganymede-SR1-win32\eclipse\eclipse.exe -vm "C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\bin\javaw" -vmargs -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Xms128m -Xmx512m
3. eclipse의 Java VM 옵션 용량 수정.
eclipse 사용시 : Window > Preferences > java > installend JREs > 사용중인 JRE선택 > edit > Default VM Arguments
기본방식
-XX:MaxPermSize=Permanent Generation의 최대용량(기본 용량은 64MB)
변경설정
-XX:MaxPermSize=128m
-출처 : Length 카페
이클립스에서 잘 돌아가고 있는데 콘솔 창에 심각! 이러면서 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space 에러가 발생하기 시작...기분 나쁜 빨간색과 띄어쓰기로 가지런히 줄지어 있는 에러들...
찾아보니 ..
'Java는 메모리 영역을 사실상 두 부분으로 구분하여 사용한다. 일반 Java Heap space와 클래스와 같이 Permenant Generation 대상 데이터를 두기 위한 PermGen space이다.
## 원인
Permanent Generation(VM이 데이터를 가지는 곳 중 하나)의 용량 부족.
## 대처
Java VM 기동 옵션에서 용량을 늘려준다.
(Eclipse의 경우는 Window->Preferences->java->installed JREs->사용중인 JRE선택 후 Edit->
Default VM Arguments에서 설정해주면 된다.)
= 기본 방식
-XX:MaxPermSize=Permanent Generation의 최대용량(기본 용량은 64MB)
= 실제 설정 시 (m은 MB)
-XX:MaxPermSize=128m
위와 같이 설정하도록 하자.
-XX:PermSize (Permanent Generation의 초기용량)을 -XX:MaxPermSize와 같은 용량으로 하는 설정도 있긴하지만 너무 적당적당히 늘려버리면 메모리 할당 균형에 문제가 생기므로 주의하자.
Permanent Generation이 부족한 경우에는 -Xmx의 사이즈도 늘리는게 좋을지도 모름
출처 -
http://netholic.tistory.com/59
요즘 들어 부쩍 java.lang.OutOfMemoryErorr로 인해 이클립스가 뻗어버리는 일이 많이 발생했었다. 하지만 Heap Monitor를 보면 200M 조차 사용하지 않는다. 이런 경우, 대부분은 PermGen 영역이 모자란 것이 원인일 수 있다.
{workspace}/.metadata/.log를 확인해보면 PermGen space라고 기록되어 있을 것이다.
Eclipse를 사용할 때는 JVM에 -Xmx 옵션은 대부분은 넣어서 사용하리라 생각한다. 하지만 Java는 메모리 영역을 사실상 두 부분으로 구분하여 사용한다. 일반 Java Heap space와 클래스와 같이 Permenant Generation 대상 데이터를 두기 위한 PermGen space이다.
대부분의 자바 애플리케이션에서는 기본 PermGen Size로 충분하겠지만 이클립스의 경우 클래스가 꽤 많아지면서 모자란 경우가 있는듯 하다. javanese의 경우 Callisto를 깔아놓고 JDT, CDT를 왔다갔다 하면서 사용하다보니 Heap은 별로 쓰지도 않는데 PermGen space가 종종 모자라는 경우가 있다. 아마 Web관련 Tool을 많이 사용하는 분도 같은 현상이 나타날 수 있을 것이다.
PermGen space는 -XX:MaxPermSize 옵션으로 설정할 수 있다.
eclipse -vm /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.5.0-sun/bin/java -vmargs -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Xms128m -Xmx512m
OutOfMemory 에러가 발생한다면 -Xmx만 늘려주지말고 PermSize도 확인해보라.
클래스 갯수가 주요원인이기보다는 최근에 framework들이 reflection을 많이 사용해서 더 큰 perm size가 꽤 필요합니다. 이클립스뿐만 아니라, WAS에도 사이즈를 늘려줘야 합니다.
출처 -
http://purehani.egloos.com/1593651
 btrace.zip
btrace.zip